Java中怎么使用線程組
這篇文章主要介紹“Java中怎么使用線程組”的相關(guān)知識,小編通過實際案例向大家展示操作過程,操作方法簡單快捷,實用性強(qiáng),希望這篇“Java中怎么使用線程組”文章能幫助大家解決問題。
讓客戶滿意是我們工作的目標(biāo),不斷超越客戶的期望值來自于我們對這個行業(yè)的熱愛。我們立志把好的技術(shù)通過有效、簡單的方式提供給客戶,將通過不懈努力成為客戶在信息化領(lǐng)域值得信任、有價值的長期合作伙伴,公司提供的服務(wù)項目有:主機(jī)域名、網(wǎng)絡(luò)空間、營銷軟件、網(wǎng)站建設(shè)、浚縣網(wǎng)站維護(hù)、網(wǎng)站推廣。
Java中線程組(ThreadGroup類)
Java中使用ThreadGroup類來代表線程組,表示一組線程的集合,可以對一批線程和線程組進(jìn)行管理。可以把線程歸屬到某一個線程組中,線程組中可以有線程對象,也可以有線程組,組中還可以有線程,這樣的組織結(jié)構(gòu)有點類似于樹的形式,如圖所示。
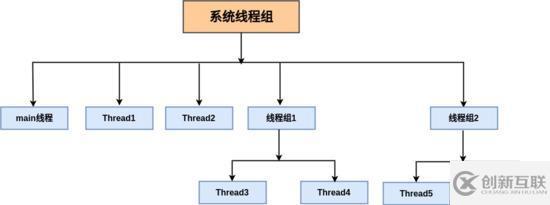
用戶創(chuàng)建的所有線程都屬于指定線程組,如果沒有顯式指定屬于哪個線程組,那么該線程就屬于默認(rèn)線程組(即main線程組)。默認(rèn)情況下,子線程和父線程處于同一個線程組。
此外,只有在創(chuàng)建線程時才能指定其所在的線程組,線程運行中途不能改變它所屬的線程組,也就是說線程一旦指定所在的線程組就不能改變。
二.為什么要使用線程組
1.安全
同一個線程組的線程是可以相互修改對方的數(shù)據(jù)的。但如果在不同的線程組中,那么就不能“跨線程組”修改數(shù)據(jù),可以從一定程度上保證數(shù)據(jù)安全。
2.批量管理
可以批量管理線程或線程組對象,有效地對線程或線程組對象進(jìn)行組織或控制。
三.線程組使用示例
1.線程關(guān)聯(lián)線程組:一級關(guān)聯(lián)
所謂一級關(guān)聯(lián)就是父對象中有子對象,但并不創(chuàng)建孫對象。比如創(chuàng)建一個線程組,然后將創(chuàng)建的線程歸屬到該組中,從而對這些線程進(jìn)行有效的管理。代碼示例如下:
public class ThreadGroupTest {
public static void main(String[] args) {
ThreadGroup rootThreadGroup = new ThreadGroup("root線程組");
Thread thread0 = new Thread(rootThreadGroup, new MRunnable(), "線程A");
Thread thread1 = new Thread(rootThreadGroup, new MRunnable(), "線程B");
thread0.start();
thread1.start();
}
}
class MRunnable implements Runnable {
@Override
public void run() {
while (!Thread.currentThread().isInterrupted()) {
System.out.println("線程名: " + Thread.currentThread().getName()
+ ", 所在線程組: " + Thread.currentThread().getThreadGroup().getName()) ;
try {
Thread.sleep(1000);
} catch (InterruptedException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
}
}
}
}
復(fù)制代碼執(zhí)行結(jié)果如下:
線程名: 線程A, 所在線程組: root線程組 線程名: 線程B, 所在線程組: root線程組 復(fù)制代碼
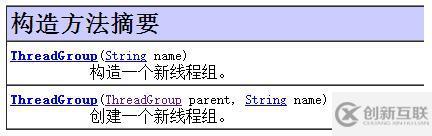
2.線程關(guān)聯(lián)線程組:多級關(guān)聯(lián)
所謂的多級關(guān)聯(lián)就是父對象中有子對象,子對象中再創(chuàng)建孫對象也就出現(xiàn)了子孫的效果了。比如使用下圖第二個構(gòu)造方法,將子線程組歸屬到某個線程組,再將創(chuàng)建的線程歸屬到子線程組,這樣就會有線程樹的效果了。
代碼示例如下:
public class ThreadGroupTest {
public static void main(String[] args) {
ThreadGroup rootThreadGroup = new ThreadGroup("root線程組");
Thread thread0 = new Thread(rootThreadGroup, new MRunnable(), "線程A");
Thread thread1 = new Thread(rootThreadGroup, new MRunnable(), "線程B");
thread0.start();
thread1.start();
ThreadGroup threadGroup1 = new ThreadGroup(rootThreadGroup, "子線程組");
Thread thread2 = new Thread(threadGroup1, new MRunnable(), "線程C");
Thread thread3 = new Thread(threadGroup1, new MRunnable(), "線程D");
thread2.start();
thread3.start();
}
}
class MRunnable implements Runnable {
@Override
public void run() {
while (!Thread.currentThread().isInterrupted()) {
System.out.println("線程名: " + Thread.currentThread().getName()
+ ", 所在線程組: " + Thread.currentThread().getThreadGroup().getName()
+ ", 父線程組: " + Thread.currentThread().getThreadGroup().getParent().getName());
try {
Thread.sleep(1000);
} catch (InterruptedException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
}
}
}
}
復(fù)制代碼執(zhí)行結(jié)果如下:
線程名: 線程A, 所在線程組: root線程組, 父線程組: main 線程名: 線程B, 所在線程組: root線程組, 父線程組: main 線程名: 線程C, 所在線程組: 子線程組, 父線程組: root線程組 線程名: 線程D, 所在線程組: 子線程組, 父線程組: root線程組 復(fù)制代碼
3.批量管理組內(nèi)線程
使用線程組自然是要對線程進(jìn)行批量管理,比如可以批量中斷組內(nèi)線程,代碼示例如下:
public class ThreadGroupTest {
public static void main(String[] args) {
ThreadGroup rootThreadGroup = new ThreadGroup("root線程組");
Thread thread0 = new Thread(rootThreadGroup, new MRunnable(), "線程A");
Thread thread1 = new Thread(rootThreadGroup, new MRunnable(), "線程B");
thread0.start();
thread1.start();
ThreadGroup threadGroup1 = new ThreadGroup(rootThreadGroup, "子線程組");
Thread thread2 = new Thread(threadGroup1, new MRunnable(), "線程C");
Thread thread3 = new Thread(threadGroup1, new MRunnable(), "線程D");
thread2.start();
thread3.start();
rootThreadGroup.interrupt();
System.out.println("批量中斷組內(nèi)線程");
}
}
class MRunnable implements Runnable {
@Override
public void run() {
while (!Thread.currentThread().isInterrupted()) {
System.out.println("線程名: " + Thread.currentThread().getName()
+ ", 所在線程組: " + Thread.currentThread().getThreadGroup().getName()
+ ", 父線程組: " + Thread.currentThread().getThreadGroup().getParent().getName());
try {
Thread.sleep(1000);
} catch (InterruptedException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
break;
}
}
System.out.println(Thread.currentThread().getName() + "執(zhí)行結(jié)束");
}
}
復(fù)制代碼執(zhí)行結(jié)果如下:
線程名: 線程A, 所在線程組: root線程組, 父線程組: main 線程名: 線程B, 所在線程組: root線程組, 父線程組: main 線程名: 線程C, 所在線程組: 子線程組, 父線程組: root線程組 線程名: 線程D, 所在線程組: 子線程組, 父線程組: root線程組 批量中斷組內(nèi)線程 線程A執(zhí)行結(jié)束 線程B執(zhí)行結(jié)束 線程C執(zhí)行結(jié)束 線程D執(zhí)行結(jié)束 復(fù)制代碼
關(guān)于“Java中怎么使用線程組”的內(nèi)容就介紹到這里了,感謝大家的閱讀。如果想了解更多行業(yè)相關(guān)的知識,可以關(guān)注創(chuàng)新互聯(lián)行業(yè)資訊頻道,小編每天都會為大家更新不同的知識點。
網(wǎng)站題目:Java中怎么使用線程組
網(wǎng)站鏈接:http://www.2m8n56k.cn/article4/jgesie.html
成都網(wǎng)站建設(shè)公司_創(chuàng)新互聯(lián),為您提供網(wǎng)站策劃、定制網(wǎng)站、Google、網(wǎng)站制作、企業(yè)網(wǎng)站制作、網(wǎng)站改版
聲明:本網(wǎng)站發(fā)布的內(nèi)容(圖片、視頻和文字)以用戶投稿、用戶轉(zhuǎn)載內(nèi)容為主,如果涉及侵權(quán)請盡快告知,我們將會在第一時間刪除。文章觀點不代表本網(wǎng)站立場,如需處理請聯(lián)系客服。電話:028-86922220;郵箱:[email protected]。內(nèi)容未經(jīng)允許不得轉(zhuǎn)載,或轉(zhuǎn)載時需注明來源: 創(chuàng)新互聯(lián)

- APP開發(fā)成本高的原因 2016-08-26
- 敢說出來嗎?究竟APP開發(fā)需要多少錢... 2022-08-07
- 來談?wù)劼眯蓄惓啥糀PP開發(fā) 2022-07-17
- 創(chuàng)新互聯(lián)APP開發(fā)公司,JAVA電商平臺開發(fā) 2022-07-31
- 成都APP開發(fā)過程中需要注意哪些方面? 2023-02-13
- 開始重視APP開發(fā)的公司越來越多 2016-08-19
- 微信小程序開發(fā)和APP開發(fā)有哪些區(qū)別? 2022-07-04
- APP開發(fā)制作價格差距大的原因分析 2023-03-14
- APP開發(fā)如何才滿足市場的需求相關(guān) 2016-11-21
- 成都在線英語學(xué)習(xí)APP開發(fā) 快樂學(xué)習(xí)英語 2022-06-01
- app開發(fā)價格公式解密 2021-03-02
- APP開發(fā)流程-佛山APP開發(fā) 2022-11-09